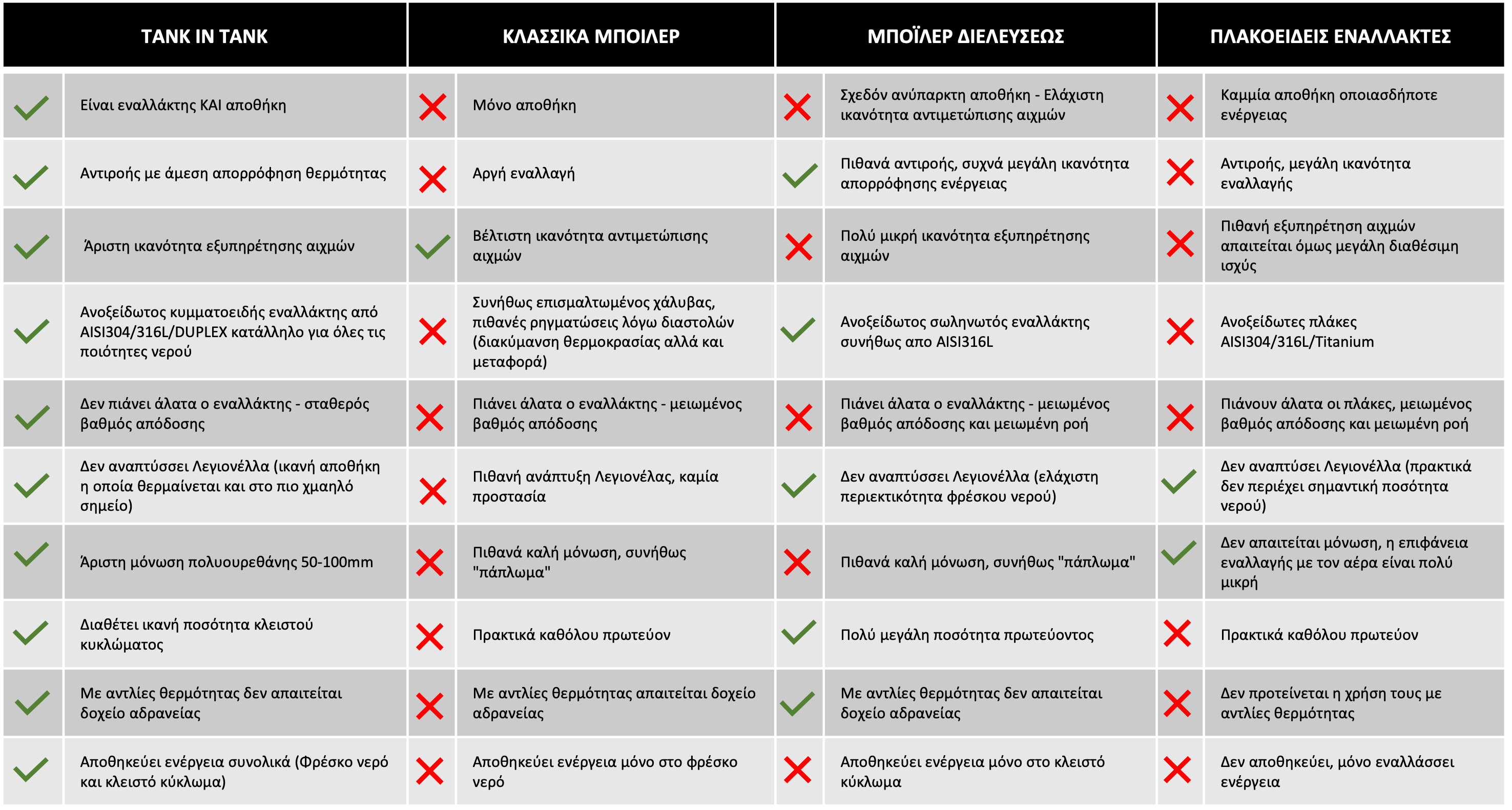
Comparison table of advantages of basic domestic water heating technologies
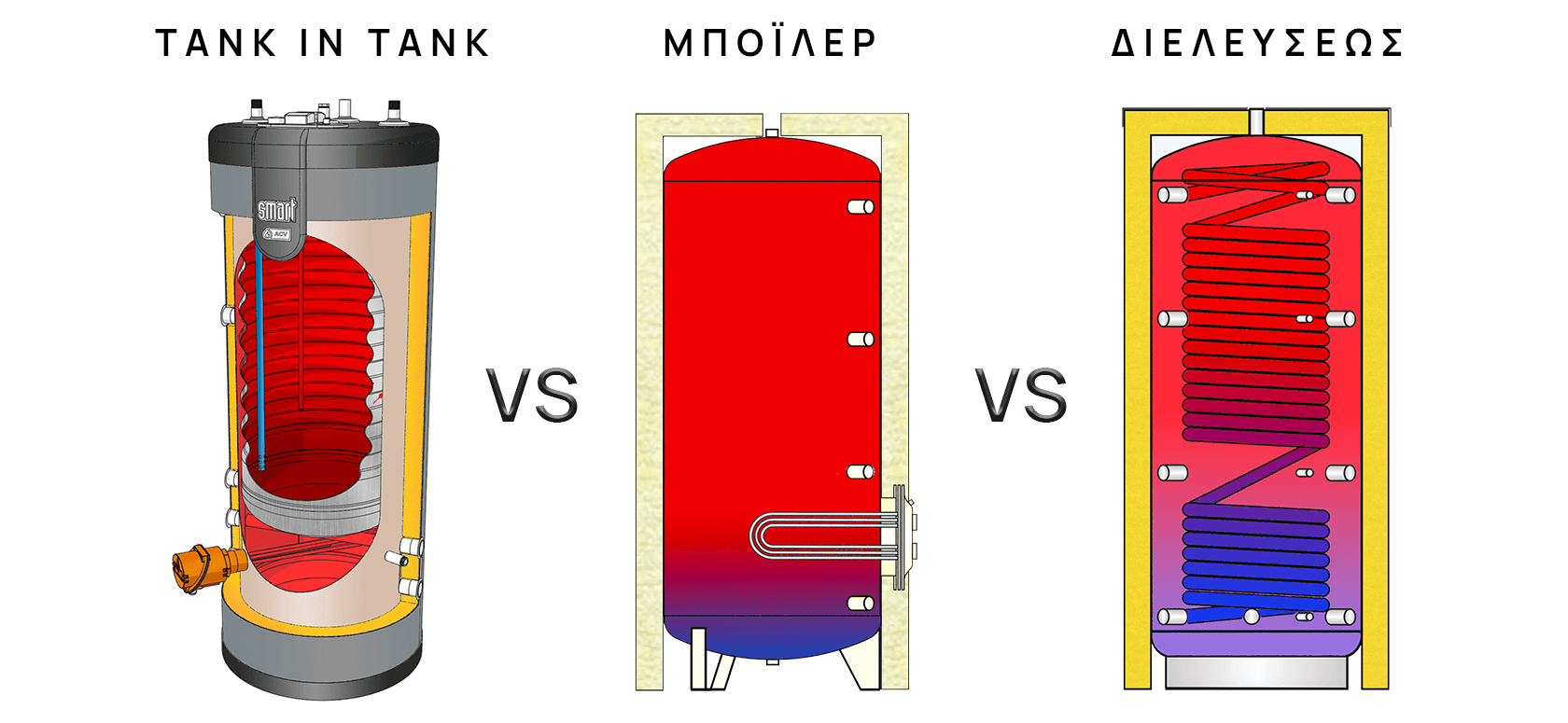
In the following table you can see in detail the advantages and disadvantages of each of the basic technologies for the production of domestic hot water (DHW). The table is followed by detailed graphs that present these points in a simple way.
What is the best way to heat water?
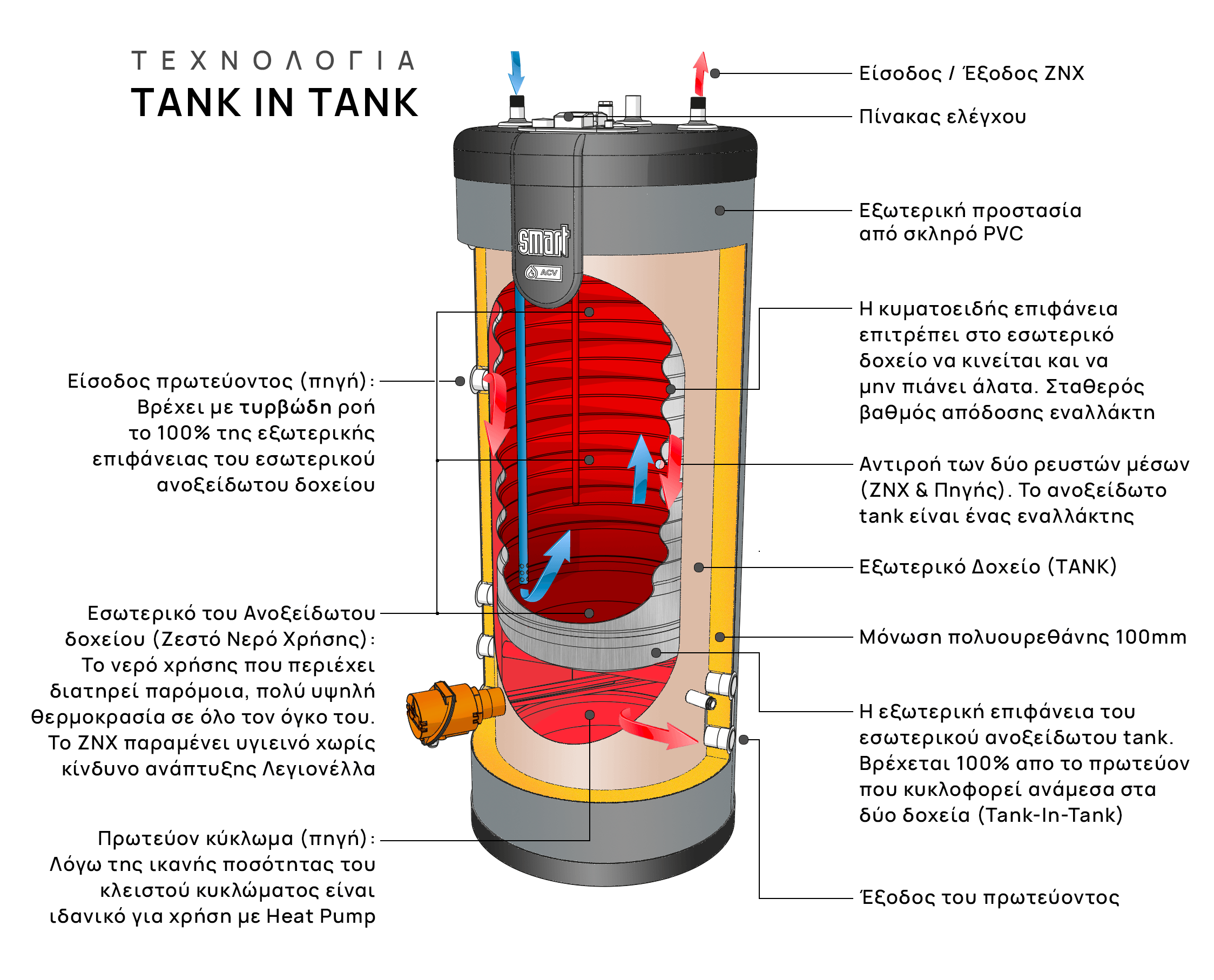
Each of these technologies has its own advantages that make it ideal for specific applications. From their detailed comparison, it emerges that the Tank In Tank system has the most advantages as it combines the high energy exchange capacity of the stainless steel exchanger with a sufficient reservoir to successfully cope with the application’s peaks.
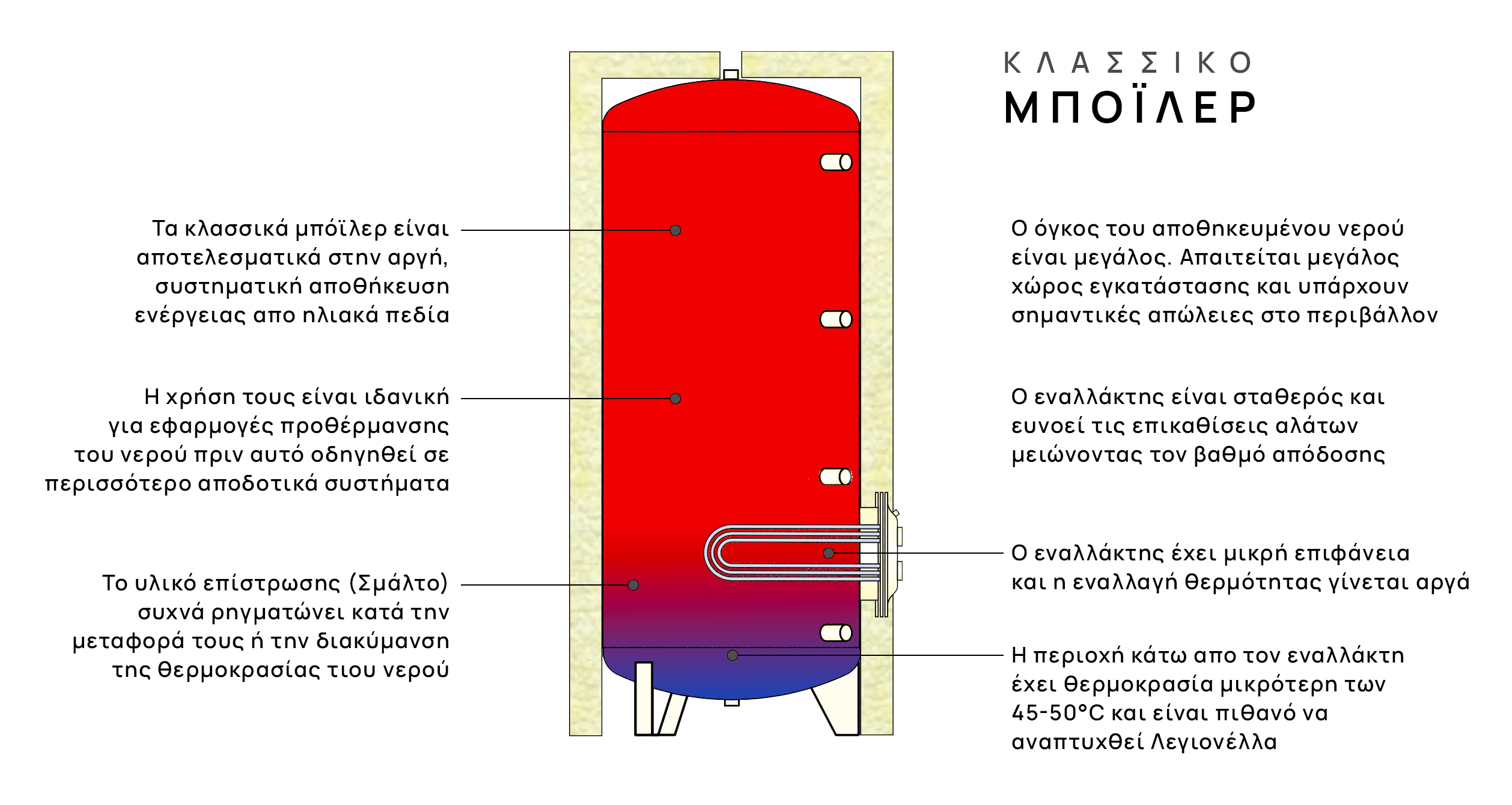
This valuable element results from the machines’ yields in Lt/10′, which is the amount of DHW that the machine can produce at its absolute peak. Although this is not a unique advantage of Tank In Tank as classic storage boilers also have this ability (but not of rapid temperature recovery), Tank In Tank additionally keeps the domestic hot water disinfected and hygienic by excluding growth Legionella, something that no conventional boiler manufacturer can ensure or, let alone guarantee.
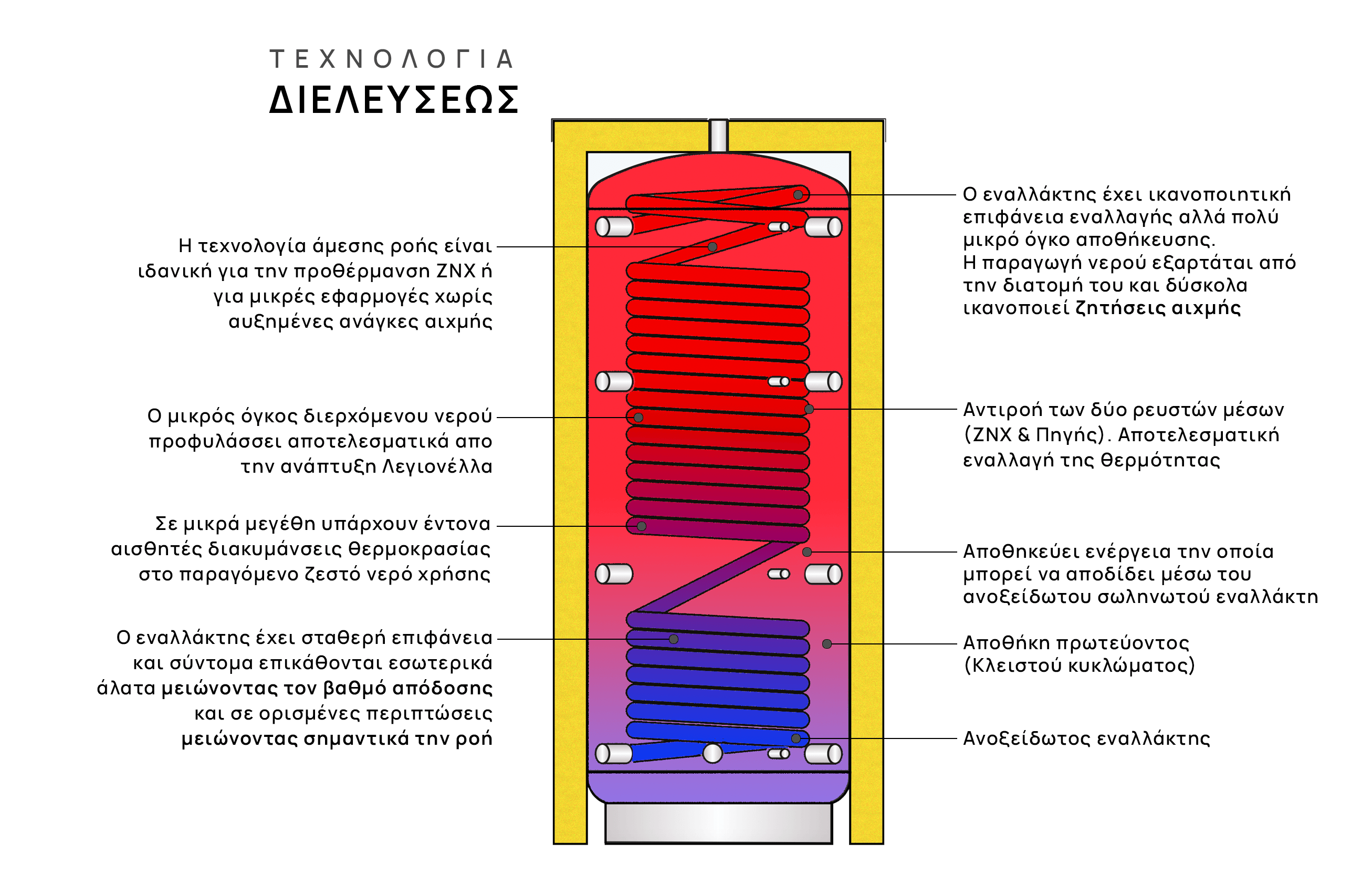
The modern technology of pass-through boilers is only effective when there is counterflow but although with the large volume of inertia of the primary they adequately cover the needs of the application in stored energy, they often lead to oversizing as the exchanger they contain is continuous flow (without significant storage) with consequently these must be over-dimensioned so that they actually cover in continuous flow (Lt/h), the peak of the application (Lt/10′).